While some people have been automating business processes for years – think hypercards and screen scraper technology – the emergence of robotic process automation (RPA) has ushered in a whole new era. Until now, automating manual processes required the time and effort of valuable systems analysts and programmers who also were needed on high-priority, mission-critical and compliance-related efforts. Automating manual tasks simply got out-prioritized. But because it doesn’t require programming, RPA makes it possible for business people to automate manual tasks, extend and amplify the capability of the back office and improve productivity with fewer resources.
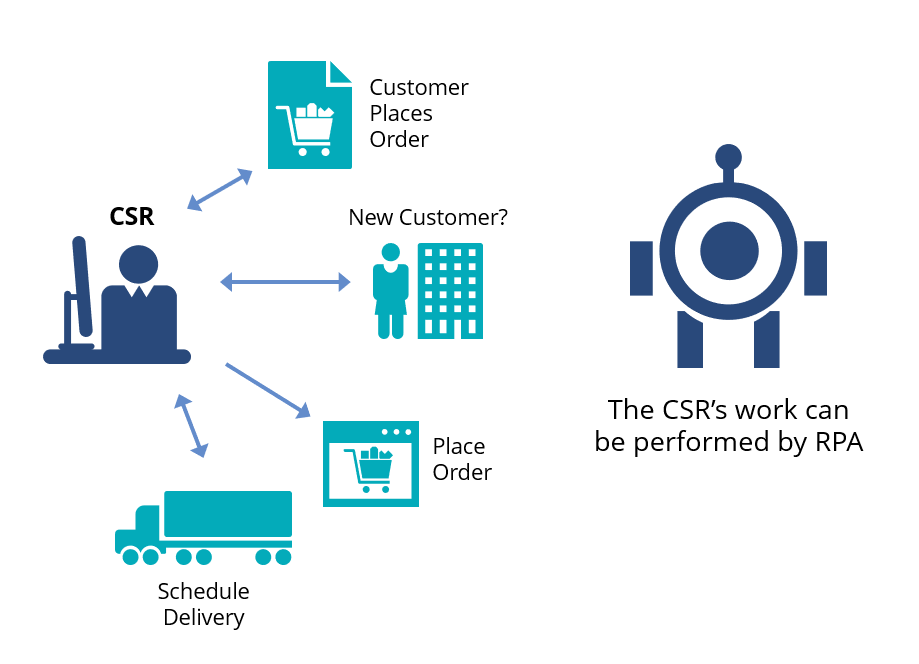
Simply defined, RPA is the automation of a task previously done by a worker. Order entry is an excellent example. Before automation, a customer service representative (CSR) receives a customer’s order and confirms if he or she has an account. If not, the CSR creates one then logs into the order system, enters the items, checks inventory and schedules the delivery. With RPA, this entire task can be automated to free up the CSR.
Like office software, automating a process with RPA consists of graphically dragging, dropping and linking icons that represent the steps in the process. Better yet, with some advanced cognitive tools, the bot can actually “learn” the task by “electronically watching” hundreds or thousands of repetitive manual entries and automatically creating its own paths. For example, bots that can render structured data from images of invoices using OCR and machine learning are yielding significant outcomes.
What Are the Benefits of RPA?
Initially, enterprises have used RPA to automate IT operations and create efficiencies and savings. Today, they are achieving much larger efficiencies and savings wherever large numbers of staff are performing highly repetitive manual work like claims processing, order entry and other related activities. The benefits of RPA are clear. Bots free up staff to focus on more complex tasks. Bots are fast, they don’t require breaks or vacation, they eliminate variations in task execution and they improve quality. In fact, some companies are seeing efficiency improvements of 30 – 70 percent. A major bank realized more than $1 million in benefits in just 90 days after it implemented RPA. A major county in the U.S. implemented RPA and dramatically improved the efficiency of administering government assistance programs and delivered an immediate return on investment.
RPA is not limited to the back office and blue-collar tasks; high level tasks can be impacted too. The New York Times reports that Kensho, a company that employs RPA for financial analysis delivers in minutes work that previously took two days for a Wall Street financial analyst to perform. Better yet, the analysis is delivered before staff arrives every day.
Some say that simply improving existing systems eliminates the need for RPA. While this sounds sensible, this question must be answered with a look at return on investment. How much time, cost and critical resources will it take to modify current systems and provide improved efficiencies, and how does that compare to the cost of RPA? In many cases, RPA has a better return on investment than modifications and enhancements using traditional methods. Even if RPA is not the long-term solution, why not implement RPA while systems are being updated and take claim to the improved efficiencies and cost savings in the meantime?
What does the market look like?
The RPA marketplace is evolving. Product features are constantly changing and new entrants are arriving in the market regularly. A sampling of current RPA vendors includes:
- AutoMate offers RPA that includes support for file/data transfers, user provisioning and report generation.
- Automation Anywhere offer RPA for business process automation that includes resilience for changes made to underlying systems.
- BluePrism offers RPA that provides support for a variety of applications and platforms.
- ipSoft offers RPA for IT service delivery that includes natural language capabilities.
- RoboTask offers RPA for repetitive PC tasks.
- UiPath offers RPA with an open, extensible architecture for highly scalable automation.
- WinAutomation offers RPA for automating desktop and web applications
- WorkFusion offers RPA for middle-office and back-office processes.
What should you do?
Determine if your team is using RPA, and if not, why not? Determine if your suppliers are using RPA and if not, why not? Then just try it. Consider candidate opportunities and pick a pilot implementation to determine the benefits. When you see benefits, attack opportunities where large numbers of staff are performing repetitive processes like order entry and claims processing. In all cases, maintain a strong focus on return on investment – that will be your real proof.
ISG helps enterprises find the right processes to automate and validate return ROI. Contact us to find out how we can help you.

